6.8 KiB
Universal Renderer
This page describes the URP Universal Renderer settings.
For more information on rendering in URP, see also Rendering in the Universal Render Pipeline.
Rendering Paths
The URP Universal Renderer implements two Rendering Paths:
-
Forward Rendering Path.
Rendering Path comparison
The following table shows the differences between the Forward and the Deferred Rendering Paths in URP.
| Feature | Forward | Deferred |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum number of real-time lights per object. | 9 Lights per object. | Unlimited number of real-time lights. |
| Per-pixel normal encoding | No encoding (accurate normal values). | Two options:
|
| MSAA | Yes | No |
| Vertex lighting | Yes | No |
| Camera stacking | Yes | Supported with a limitation: Unity renders only the base Camera using the Deferred Rendering Path. Unity renders all overlay Cameras using the Forward Rendering Path. |
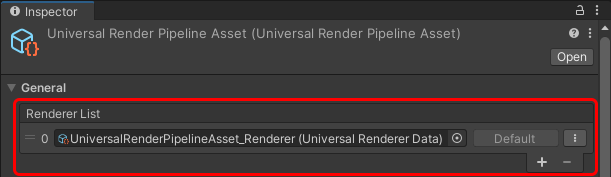
How to find the Universal Renderer asset
To find the Universal Renderer asset that a URP asset is using:
-
Select a URP asset.
-
In the Renderer List section, click a renderer item or the vertical ellipsis icon (⋮) next to a renderer.
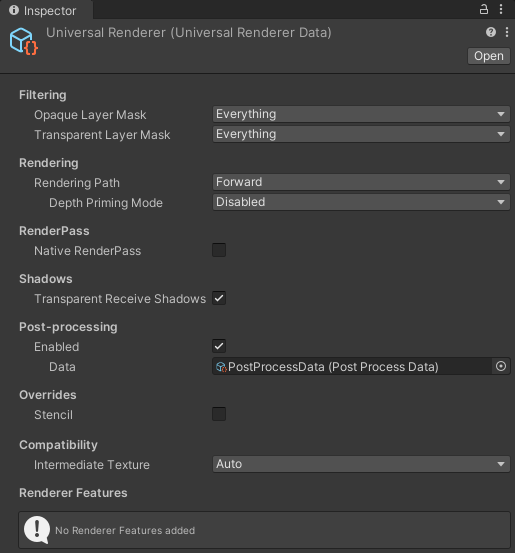
Universal Renderer asset reference
This section describes the properties of the Forward Renderer asset.
Filtering
This section contains properties that define which layers the renderer draws.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Opaque Layer Mask | Select which opaque layers this Renderer draws |
| Transparent Layer Mask | Select which transparent layers this Renderer draws |
Rendering
This section contains properties related to rendering.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Rendering Path | Select the Rendering Path. Options:
|
| Depth Priming Mode | This property determines when Unity performs depth priming. Depth Priming can improve GPU frame timings by reducing the number of pixel shader executions. The performance improvement depends on the amount of overlapping pixels in the opaque pass and the complexity of the pixel shaders that Unity can skip by using depth priming. The feature has an upfront memory and performance cost. The feature uses a depth prepass to determine which pixel shader invocations Unity can skip, and the feature adds the depth prepass if it's not available yet. The options are:
This property is available only if Rendering Path is set to Forward |
| Accurate G-buffer normals | Indicates whether to use a more resource-intensive normal encoding/decoding method to improve visual quality. This property is available only if Rendering Path is set to Deferred. |
| Copy Depth Mode | Specifies the stage in the render pipeline at which to copy the scene depth to a depth texture. The options are:
|
Native RenderPass
This section contains properties related to URP's Native RenderPass API.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Native RenderPass | Indicates whether to use URP's Native RenderPass API. When enabled, URP uses this API to structure render passes. As a result, you can use programmable blending in custom URP shaders. For more information about the RenderPass API, see ScriptableRenderContext.BeginRenderPass. Note: Enabling this property has no effect on OpenGL ES. |
Shadows
This section contains properties related to rendering shadows.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Transparent Receive Shadows | When this option is on, Unity draws shadows on transparent objects. |
Overrides
This section contains Render Pipeline properties that this Renderer overrides.
Stencil
With this check box selected, the Renderer processes the Stencil buffer values.
For more information on how Unity works with the Stencil buffer, see ShaderLab: Stencil.
Compatibility
This section contains settings related to backwards compatibility.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Intermediate Texture | Controls when URP renders via an intermediate texture. Options:
|
Renderer Features
This section contains the list of Renderer Features assigned to the selected Renderer.
For information on how to add a Renderer Feature, see How to add a Renderer Feature to a Renderer.
URP contains the pre-built Renderer Feature called Render Objects.